Jaw joint disorders encompass a variety of conditions that affect the jaw muscles, ligaments, and bone structures. Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders commonly present with symptoms such as jaw pain, clicking sounds, restricted jaw movement, and headaches. Causes of these disorders include structural abnormalities, degenerative processes, and psychological stress. Treatment typically begins with conservative approaches based on physical therapy to reduce pain and improve function. In advanced cases, surgical interventions such as arthroscopy or prosthetic joint reconstruction are preferred to enhance outcomes.

Temporomandibular joint disorders present with symptoms of varying severity and can have significant effects on surrounding tissues. These disorders manifest through various discomforts in the head, neck, and jaw areas. Jaw pain and tenderness are the most common symptoms of TMJ disorders and can make daily movements challenging.
These symptoms may appear in different combinations in individuals, and some people may experience a broader range of discomfort beyond a single symptom. Prolonged symptoms such as pain or sounds can negatively impact a person’s quality of life. In untreated cases, there is a risk of symptom escalation and potential damage to surrounding tissues.
Temporomandibular joint disorders are caused by various factors, leading to structural and functional disruptions in the jaw joint. Major factors include jaw trauma, arthritis, bruxism, and stress. Each factor impacts the joint differently, causing pain, restricted movement, and inflammation.
Additional risk factors may also influence TMJ disorders. Connective tissue disorders, such as Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, can lead to joint instability, increasing the risk of pain and loss of function. Chronic habits place continuous pressure on the joint, accelerating the development of TMJ disorders.
*We recommend that you fill in all fields so that we can get back to you in the best possible way.
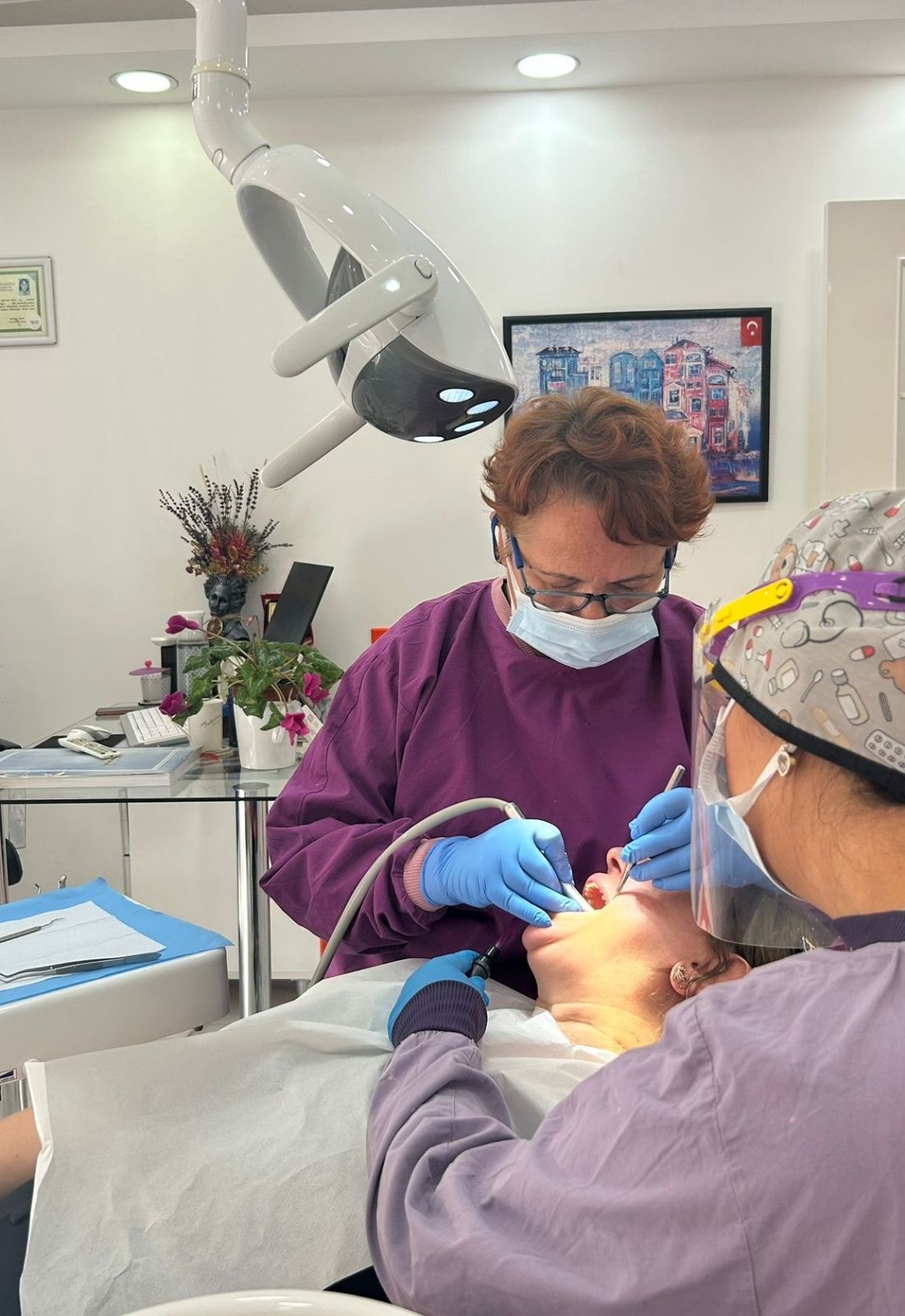
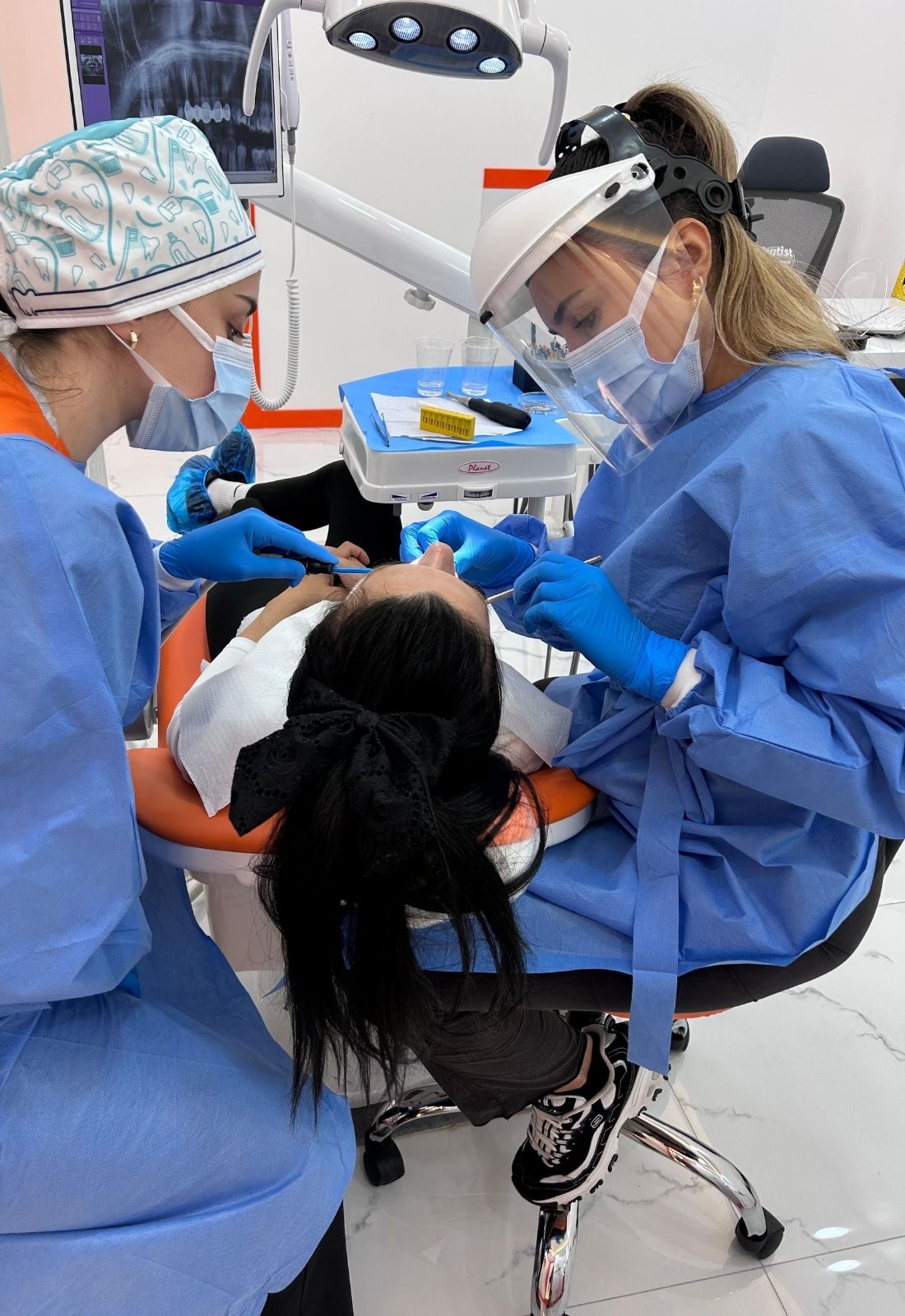
The diagnosis of jaw joint disorders is performed through a comprehensive evaluation process. First, the patient’s medical history is reviewed to identify past traumas or habits that may affect the jaw joint. The patient’s symptoms are thoroughly assessed, including related symptoms such as earache or headache.
Next, a physical examination is conducted to assess jaw movement; abnormal sounds, such as clicking, popping, or grinding, are noted. Tenderness in the jaw, neck, and head muscles is evaluated. During this examination, the range of jaw movement is tested, and any deviations or difficulties are observed. The physician palpates muscle groups, such as the masseter and temporalis, to identify trigger points.
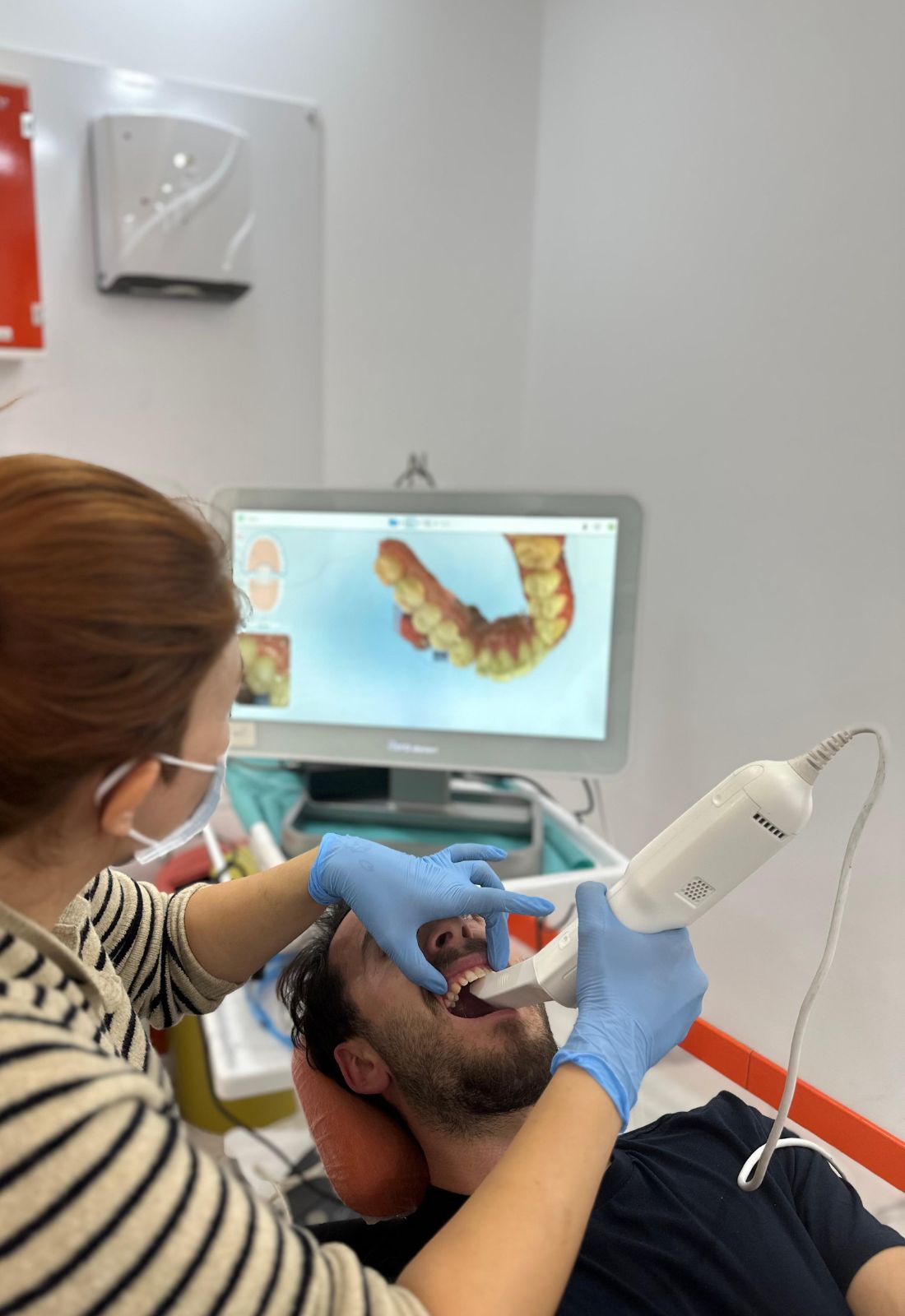
If sufficient information cannot be obtained from the physical examination, or if structural issues are suspected, imaging methods are used. X-rays and CT scans are utilized to examine the bony structures of the joint, while MRI is preferred for assessing soft tissues. MRI is particularly useful for detecting dislocation or degeneration of the joint disk.
Surgery for temporomandibular joint disorders is generally considered a last resort for severe cases where other treatment options have proven inadequate. These cases involve persistent pain, structural damage to the joint, or significant functional loss, such as jaw locking. Surgical intervention is particularly indicated for patients whose joint anatomy has been damaged due to arthritis, dislocation, or bone deformities.
The main surgical options for TMJ are:
Arthroscopy, a minimally invasive procedure, is performed with a camera and instruments inserted into the joint, reducing recovery time and the risk of complications. Arthrocentesis, a simpler technique, involves inserting a needle into the joint to relieve inflammation and limited movement. This method is considered before more extensive surgical interventions.
Open joint surgery, the most invasive procedure, requires a large incision to access the joint directly and is typically used for severe deformities or tumors. Although recovery time is longer, this method also carries risks of complications such as nerve damage and jaw stiffness.
Joint replacement is performed in advanced cases where the joint structure is severely damaged, and it is generally suitable for older adults. Each surgical option is selected based on the patient’s needs and the severity of the TMJ disorder. The risks and outcomes of surgery are carefully evaluated, and surgery is considered only when non-surgical treatments are insufficient.



The management and prevention of jaw joint disorders can be achieved through various changes and habits that individuals can incorporate into their daily lives. Reducing stress, correcting posture habits, and minimizing excessive jaw movements can prevent the development of TMJ disorders or alleviate existing symptoms. Personal precautions to maintain TMJ health include the following recommendations:
These strategies help reduce pressure on the TMJ, promoting comfort in jaw movements. Daily activities such as jaw exercises and mindfulness practices help relax muscles and support joint function. Hot and cold therapies effectively reduce inflammation and pain, providing a soothing effect.
Additionally, regular dental check-ups are important for assessing TMJ health and seeking professional treatment if necessary. In advanced cases, minimally invasive procedures or arthrocentesis can help alleviate persistent symptoms.



To schedule an appointment, please complete the form below in full and contact us.

19 Ağız ve Diş Sağlığı Merkezimiz ile İzmir’in her yerinde hizmetinizdeyiz.
Tüm Hakları Saklıdır | Özel Avrupadent Ağız ve Diş Sağlığı Hastaneleri
